10 January 2022
[Introduction to the Competition]
The 2021 Delta International Solar Building Design Competition was hosted by International Solar Energy Society, China Renewable Energy Society and China Architecture Design & Research Group, organized by China National Engineering Research Center for Human Settlements and Specialized Committee on Solar Building of China Renewable Energy Society, and sponsored by Delta Group.
Topic of the Competition was "Sunshine • Low-carbon Community". The competitors were required to focus on the carbon emission peak goal of 2030 and carbon neutralization goal of 2060, implement the national transformation of energy utilization, promote the development of low-carbon society, build a green and healthy living environment, and integrate the concept of low-carbon, green and sustainable development into community construction.
Different from the Competition held in previous years, this year's Competition featured a combination of site construction and conceptual design, i.e., the construction project of Low-carbon Community of Dongga Village, Qinglong Township, Bangor County, Tibet and the conceptual design project of "zero-carbon community". 149 pieces of works were collected for the 2 projects from all over the world. After 3 rounds of review and appraisal by the Panel of Reviewers made of up 10 top academic experts from home and abroad, led by Academician Cui Kai, a total of 2 first prize winners, 4 second prize winners and 8 third prize winners were selected.
Since the Competition was held the first time, it has been promoting innovative practice in application of solar technologies. In the research, renewable energy technologies such as solar energy were used to explore paths to "low-carbon communities" in the urban and rural construction, so as to build solar buildings into real buildings that are durable and of viewing value, and allow the public to feel and see the demonstration buildings. The ultimate goal is to promote application of green building technologies like green energy to buildings, and improve people's living standard with science and technology.
The final review meeting of 2021 Delta International Solar Building Design Competition with the topic "Sunshine · Low-carbon Communities", held in response to the "Carbon Neutrality and Emission Peak" goal, was held on January 10, 2022. After the intense exhibition and defense, the works named Sinking Street and House, completed by Li Ruichen, He Jiaqi, Xie Chong, Ran Chengli and Wang Wenxuan, students of the Faculty, under guide of Li Tiejun, Zhang Haibin and Li Zhenze, teachers of the Faculty, claimed the first prize for real construction project with the highest total score. Besides, the works Light · Cave and Sunny Side were given the third prize; works Halo · Hidden Cavity, Warm Room - Gathering Energy, and Carbon Fixation · Energy Transfer were given the honorable mention.

[Introduction to the first-prize-winning works]
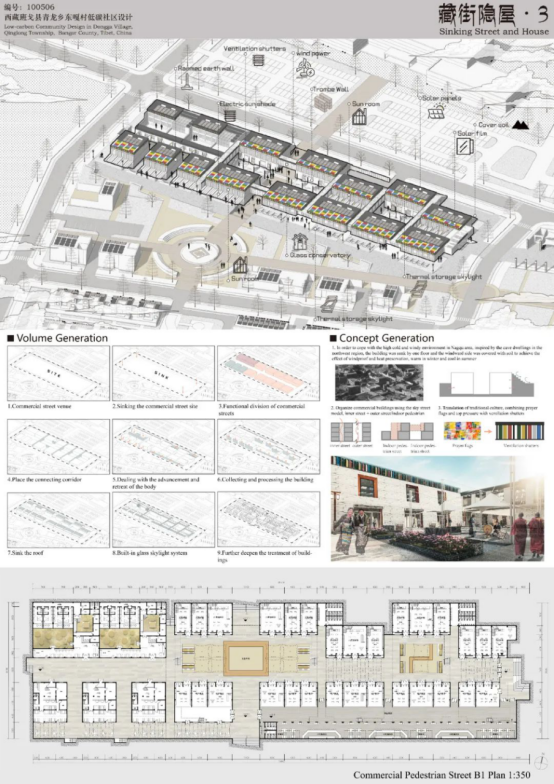
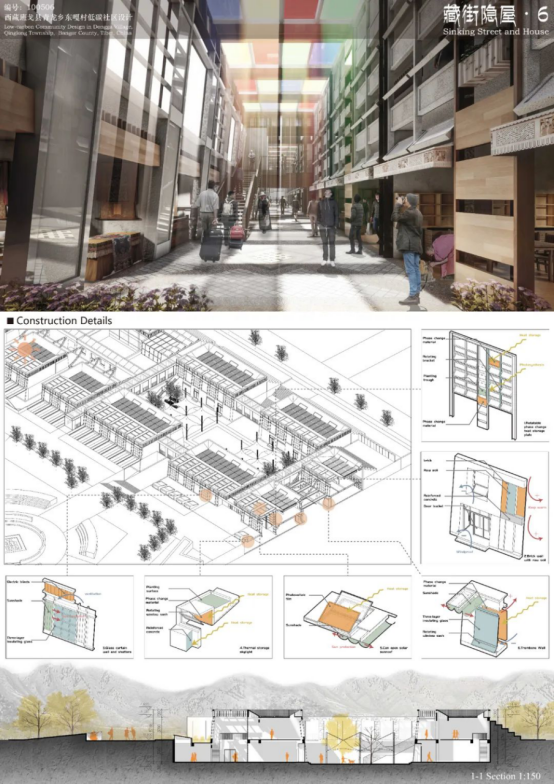
The design was inspired by traditional cave dwellings, and features subsidence of building and backfill covering to improve wind resistance and thermal insulation; besides, the modern sky-street-type commercial space was introduced by leading the main inner streets and shop fronts into the sun rooms and sun galleries, to build a diversified pedestrian system and public space. Technically, the rammed earth walls and soil-interlayer brick walls were built using local materials. New technologies such as sun room, color thin-film photovoltaic panel, dark solar crystalline silicon panel, heat storage skylight, color ceiling louver, and phase change heat storage panel were used in close combination with the traditional Tibet-style architectural image. The design involves the following 8 aspects:
00 Concept

The vast and colorful Qinghai-Tibet Plateau is the earth's third pole. Here, a riot of natural colors blend into a widely-known cultural symbol of Tibet, the flying prayer flags of different colors, which are inspiring the architectural design in Tibet in modern times.
We decided to build a colorful new home for Tibet people In a low-carbon community that combines the unique cultural elements and symbols of Tibet with modern technologies.
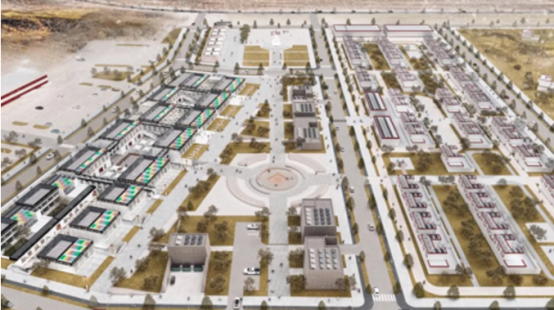
01 Overall planning
The project site is located in Qinglong Township, Naqu City in the desert on the north side of Namtso. The climate conditions here are severe, with cold and dry air throughout the year. The minimum temperature here is -28°, with prevailing wind direction of northwest wind and annual hours of sunshine of 2,800h.
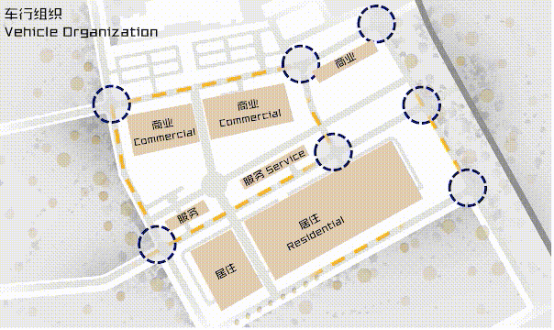
In view of the existing conditions and the required functional division, we set up the two axes, landscape and function, the intersection of which was determined as the cultural square of the future community; the service relation among the four functional sections was determined based on the nature of two groups, visitors and Tibet people.
To guide the people movement toward the business district and the central axis, a pedestrian system runs through the project, around which there is a driveway. The layout of buildings was designed taking into account the natural conditions and local styles.
02 Volume & functions
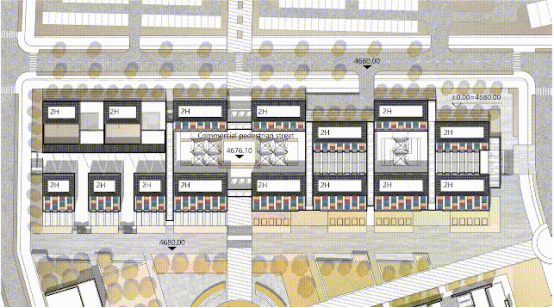
In the in-depth design of the business street, in order to meet the thermal insulation requirements, the overall building was subsided. The excavated earth was piled up on the north side to improve wind resistance. The main shopping activities were located on the west side with better accessibility. In order to further reduce heat loss, the individual units were connected to form a street to get a lower shape coefficient. The volume was reduced to create a Tibet style. In the last step, the external PV components, skylight system and roof were combined into one piece.
The outer street on the first floor has a versatile external space. The inner street and shop fronts are led into the sun rooms and sun galleries. Similarly, different shop modes were designed using the low-carbon technologies to build a pleasant and colorful sky-street-style commercial space.
03 Technological system
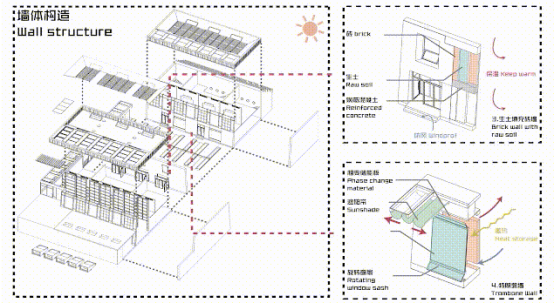
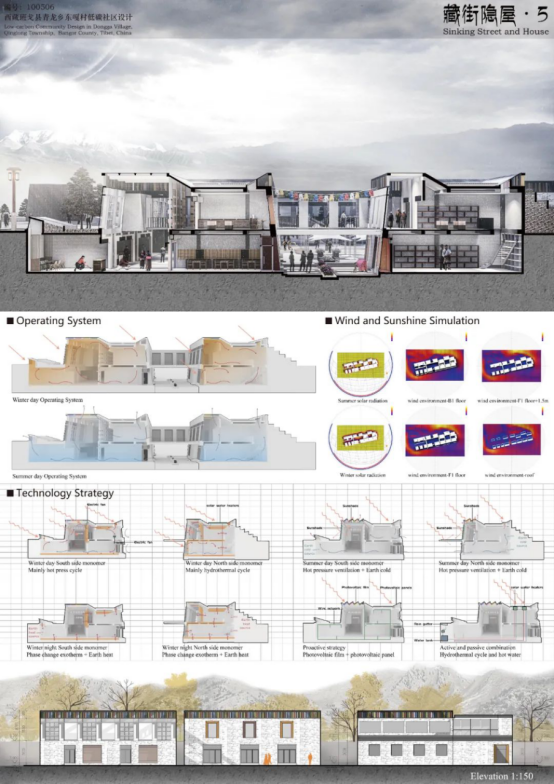
In view of the climate of the region and building characteristics, including low temperature in winter, strong radiation in summer, strong northwest wind and poor lighting we proposed the use of corresponding technical systems and component design.
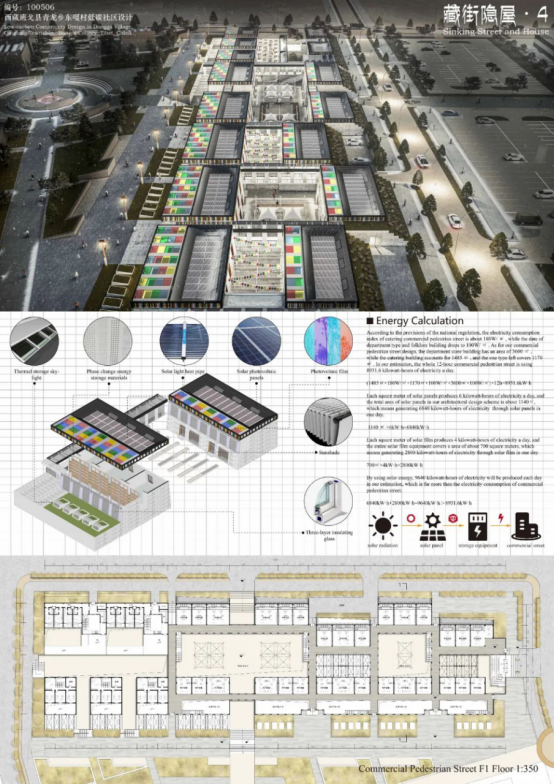
The detailed design of technical components mainly included 3 types: the main components of sun room, including the side wall of the room and phase-change thermal storage movable board wall; enclosure components, including the Trombewall and raw soil filled brick wall of the building; and skylight, including photovoltaic film skylight and phase-change heat storage skylight. All the movable components are under centralized control of intelligent control APP. With use of environmental monitoring and building component control panel, intelligent control of low-carbon and health environment is realized.
04 Passive technology

The passive system was adopted to ensure a comfortable indoor thermal environment in different seasons.
During daytime in winter, sunlight is utilized to heat up the sun room and Trombewall. Terrestrial heat is utilized to keep the basement spaces warm. The indoor air circulates under action of hot pressure and heats up the phase-change materials to meet the thermal insulation requirements.
During nighttime in winter, the phase-change materials and underground soil give out heat constantly to keep the room warm.
During daytime in summer, the first ground floor remains cool. The abat vent above the sun room is deployed to block excessive sunlight. The indoor air, under the action of hot pressure, circulates through the louver vents, doors and windows to provide indoor ventilation.
05 Active technology

Lighting, heat pump and draught fans of the building are all powered by PV power supplies. Surplus power is enough to meet the consumption of the residential area and supporting areas. The active components in the sun room, including the electric louver and rotatable phase-change energy storage board, can be used to regulate the indoor climatic environment.
To ensure a comfortable thermal environment of the building, the ground source heat pump and flat plate collector are used, drawing on the solar energy and terrestrial heat to meet the heat requirements of the building in different periods of time.
The simulation calculation showed that the annual electric energy production of the business street would be 434,000 kwh, which means a surplus of 108,000 kwh after meeting the power needs of the building itself and the community.
06 Low-carbon technology
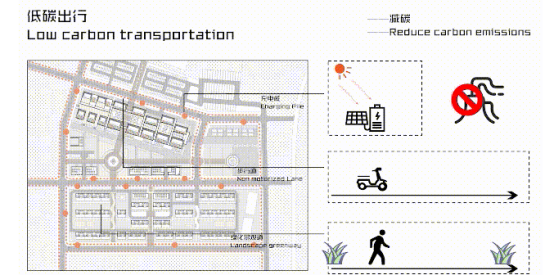
Five low-carbon strategies were used for the entire community, which would result in an annual reduction in carbon dioxide emission of 512 tons.
As for use of clean energy, the use of various PV components and wind power generation can meet various power consumption requirements.
As for thermal insulation and energy saving of the building, heat supply during daytime is met with the use of sun room and Trombewall. The ground source heat pump and phase-change materials give out heat during nighttime to meet the heat supply requirements.
As for construction and transportation, the excavated earth is used for earth covering and landscaping of the building, significantly saving cost of building materials and earth transportation.
As for the road and traffic system, the solar charging piles, electric vehicle lanes and green sidewalks are set up to encourage low-carbon travel.
As for forest carbon sinks, trees and shrubs suitable for the local climate were selected for the landscape green space.
07 Scene exploration

Drawing exhibition


Video of the complete presentation
